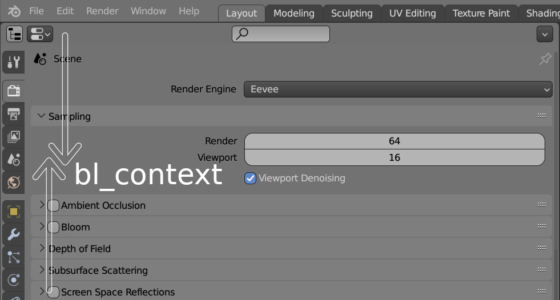
Custom Icons for EnumProperty in Blender
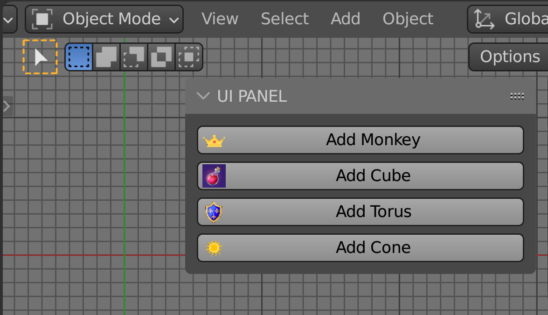
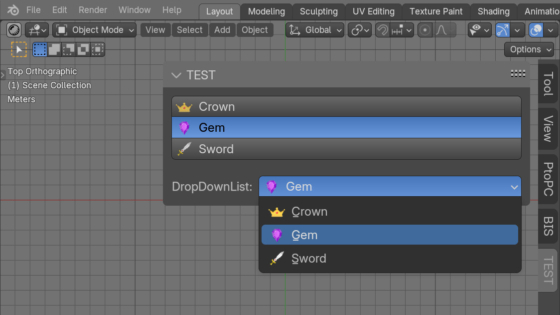
We can use custom icons, icons loaded from external files, and not embedded in Blender libraries, for example, to add customization to operator call buttons in UI panels. However, it is not only buttons that may require custom icons. Using the Blender Python API, we can add customization to drop-down list items or switches that are created based on the EnumProperty type.
 .blend file on Patreon
.blend file on Patreon