Blender
Creating controls for visually controlling the TimeLine start and end frames number in Blender
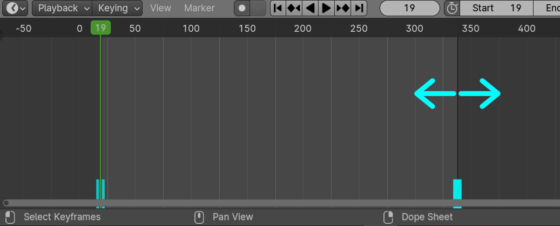
In general, gizmos looks like arrows and circles on a 3D object with which we can move, rotate and scale the mesh. However, in Blender, the gizmo object is more versatile and can be used to suit our needs in different workspaces. For example, we can create a gizmo to adjust the start and end points of the timeline.
Blender add-on: BIS v. 1.11.1
BIS (Blender Interplanety Storage) updated to v.1.11.1.
- Add-on updated for compatibility with Blender 4.0.
Creating procedural blue marble material in Blender
Creating procedural blue marble material in Blender by Ryan King Art.
Enabling and disabling collections by object
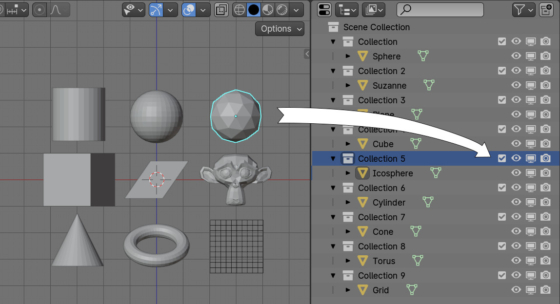
We can enable or disable a collection that contains a specific object using the Blender Python API with a simple script. For example, let’s turn off the collection in which the currently selected object is.
Changing the number of visible channels in Blender Video Editing
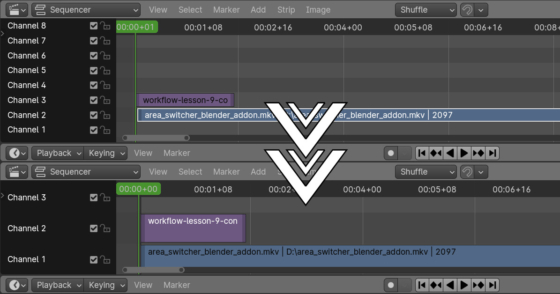
By default, there are 7 lines allocated for displaying channels with strips in the Blender user interface, in the Video Sequencer area. If all of them are not used in video editing, it will not be possible to hide unnecessary ones by simply scaling the area size.
However, this can be done by scaling the entire area interface.
Changing the number of visible channels in Blender Video EditingRead More »
BlendPyBridge – Microsoft Visual Studio Code extension for developing Blender add-ons
BlendPyBridge is the Visual Studio Code extension, designed to simplify the development of Blender add-ons. For those developers who use the “Blender Development” VSC extension, it can be an interesting alternative.
BlendPyBridge – Microsoft Visual Studio Code extension for developing Blender add-onsRead More »
Creating procedural Saturn planet material in Blender
Creating procedural Saturn planet material in Blender by Ryan King Art.
 Buy on Blender Market
Buy on Blender Market Buy on Gumroad
Buy on Gumroad Get on Patreon
Get on Patreon