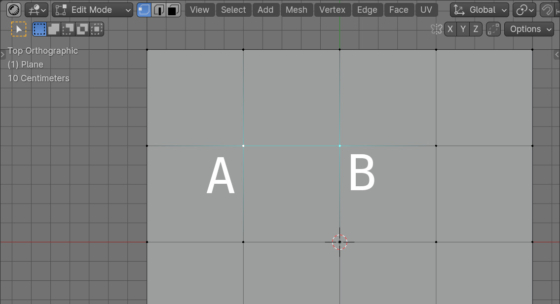
Getting paths to Blender startup files
For different work directions in Blender, separate startup configurations are organized – sets of basic settings for scene parameters, rendering and user interface. Each configuration is stored in a separate file and is loaded from it when the user opens Blender or executes the “File – New” command from the main menu.
 .blend file on Patreon
.blend file on Patreon