Blender
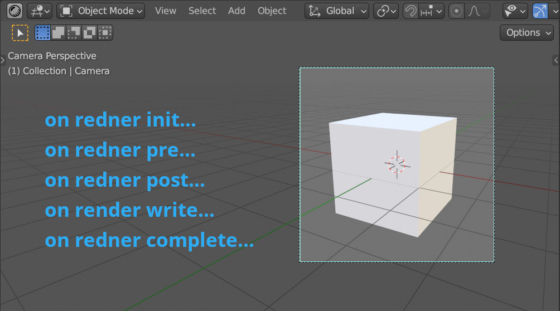
Render event order
To execute some actions at different stages of rendering, the developers have provided a set of handlers in the Blender Python API – special functions for handling events.
Creating procedural buffalo plaid fabric
Creating procedural buffalo plaid fabric material in Blender by Ryan King Art.
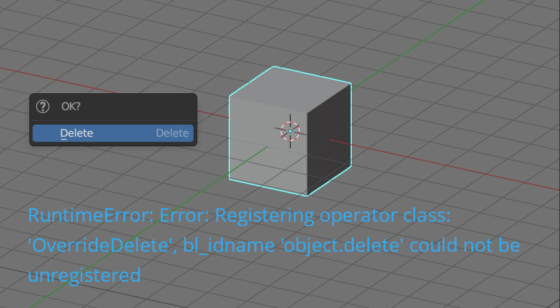
Overriding base operators in Blender 3.5 Python API is disabled
Since Blender 3.5 version, the Python API does not allow overriding base operators.
Overriding base operators in Blender 3.5 Python API is disabledRead More »
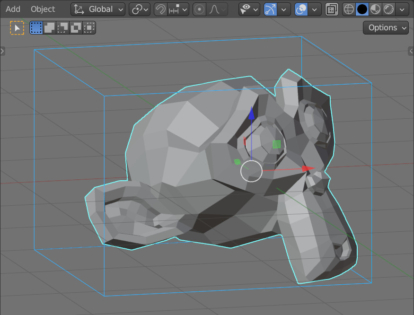
Counting AABB for object in Blender
For quick and rough checking of two objects geometry intersections, bounding objects are usually used – spheres or parallelograms in which all points of the object are inscribed. Bounding object intersections are often inaccurate, but they are very efficient in terms of speed. One of the types of bounding objects is AABB (Axis Aligned Bounding Box) – a parallelogram aligned with the global coordinate axes.
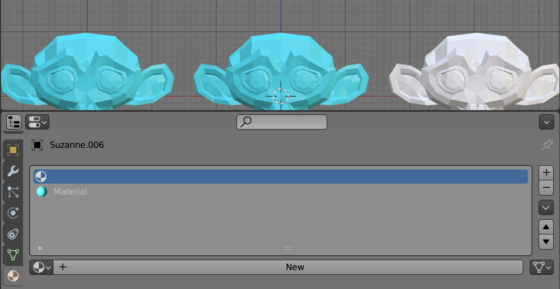
Selecting objects with no materials
For quickly finding and selecting objects that do not have materials, we can use the Blender Python API and write a script consisting of just a few lines.

 .blend file on Patreon
.blend file on Patreon
 Buy on Blender Market
Buy on Blender Market Buy on Gumroad
Buy on Gumroad