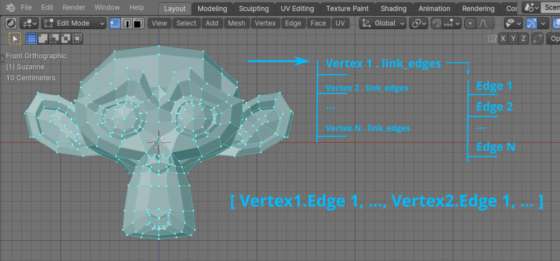
Getting a list of data from object properties using list comprehension
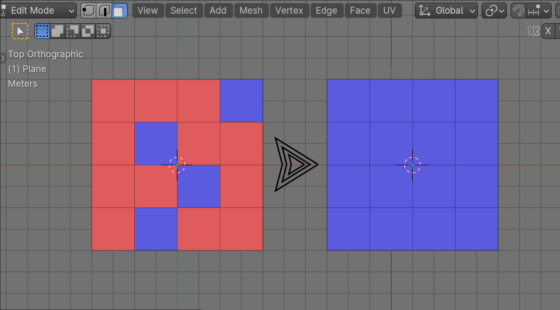
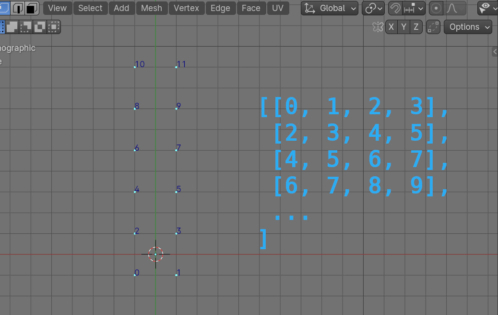
Most objects in Blender have multiple lists of data in their structure. For example, inside a “mesh” object there are list with vertices of this mesh, the list of mesh edges, and the list of mesh polygons. And in the structure of each mesh vertex there is, for example, a list with its coordinates along the X, Y and Z axes.
Getting a list of data from object properties using list comprehensionRead More »
 .blend file on Patreon
.blend file on Patreon

 Buy on Blender Market
Buy on Blender Market Buy on Gumroad
Buy on Gumroad