How to switch between flat and smooth shading through the Blender Python API
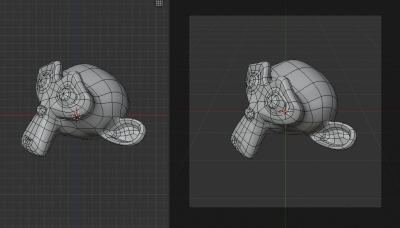
The flat/smooth shading mode is regulated through the “use_smooth” property of each polygon of the mesh.
To enable smooth shading we need to set the “use_smooth” property of each mesh polygon to “True”.
For active object:
|
1 |
bpy.context.object.data.polygons.foreach_set('use_smooth', [True] * len(bpy.context.object.data.polygons)) |
To enable flat shading – set the “use_smooth” property of each polygon to “False”.
|
1 |
bpy.context.object.data.polygons.foreach_set('use_smooth', [False] * len(bpy.context.object.data.polygons)) |
To make new shading mode visible – force update mesh data:
|
1 |
bpy.context.object.data.update() |