4.1
Working with Mean Bevel Weight using the Blender Python API
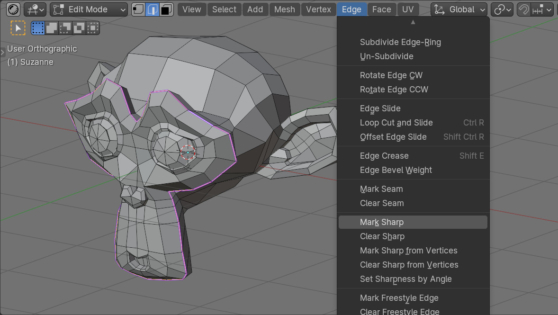
To interact with the Bevel modifier, which creates a bevel on specified edges, each of the required edges must be given a specific numeric weight parameter ranging from 0.0 to 1.0. In manual mode, the weight for the bevel is set in the N-panel on the Item tab in Edges Data – Mean Bevel Weight field. This weight can also be read and set via the Blender Python API.
Working with Mean Bevel Weight using the Blender Python APIRead More »
Working with sharp edges using Blender Python API
In Blender, we can mark the edges of the mesh as sharp so that they remain sharp and do not become smooth even when we enabling smooth shading. This can be done manually by selecting the desired edges and pressing the Edge – Mark Sharp items in the main menu. Edges can also be marked as sharp using the Blender Python API.
Working with sharp edges using Blender Python APIRead More »
Working with mesh edges marked for rendering using the Freestyle render engine
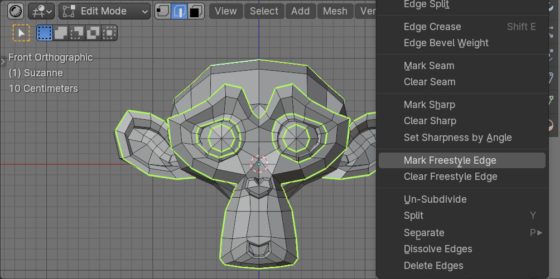
To create line-based renderings, such as blueprints or 3D to 2D stylizations, an additional “Freestyle” render engine is usually used with the main render engine. Edges that should be clearly outlined in the final render must be marked as “freestyle” so that the Freestyle render engine can process them.
Working with mesh edges marked for rendering using the Freestyle render engineRead More »
Batch export to OBJ from Blender
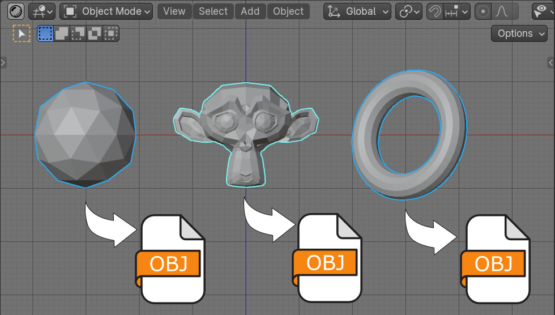
We can export any mesh from Blender to a file in OBJ format by selecting it and pressing the following items from the main menu: FIle – Export – Wavefront (.obj). If we need to split the scene into objects and export each of them to OBJ, this process can be easily automated.
Recalculating mesh normals using the Blender Python API
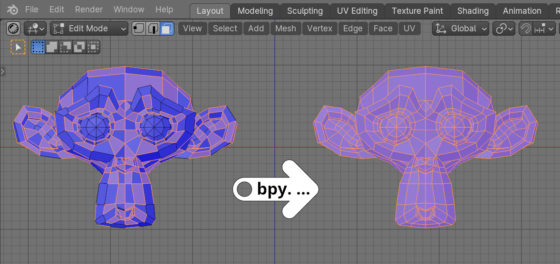
In order to quickly “recalculate the normals” – change the direction of the normals so that they are all directed towards the outer surface of the mesh, using the Blender Python API, we can create a script consisting of just a few lines of code.
Recalculating mesh normals using the Blender Python APIRead More »
Simple dynamic LOD in Blender
One of the popular methods for speeding up rendering 3D scenes is to use LOD – Level Of Details. When using LOD, objects close to the camera have the highest detail, midgrounds have medium detail, and backgrounds objects are very rough and undetailed because they are still almost invisible. Such a scene is rendered much faster than a scene in which all objects have maximum detail.
Blender add-on: M-Cleaner v. 1.4.0
Blender add-on “M-Cleaner” updated to v. 1.4.0.
- Added an option don’t to “merge by name” hidden materials (material name stars with dot).
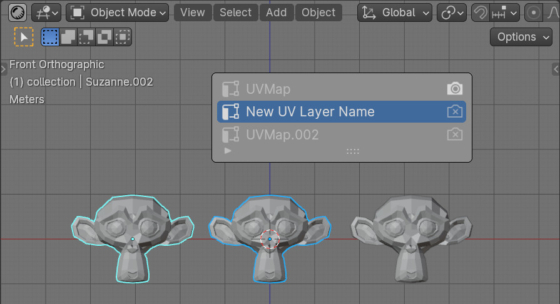
Quickly rename the UV layer for all selected objects in Blender
If we need to quickly rename the desired UV Layer for all selected objects in Blender, we can use a simple Python API script to do this in a one button press.
Quickly rename the UV layer for all selected objects in BlenderRead More »
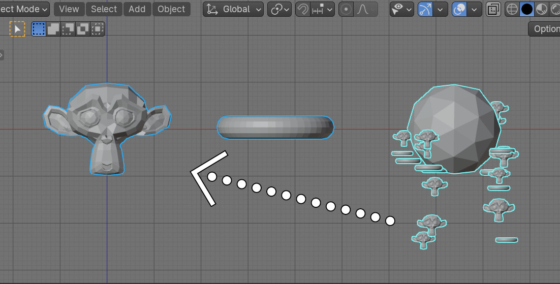
Determining which object is the source for a particle in the Particle System when using collections
If a particle system uses a collection with different meshes as its source, we can use the Blender Python API to determine which object is the source of each particle.
 Buy on Blender Market
Buy on Blender Market Buy on Gumroad
Buy on Gumroad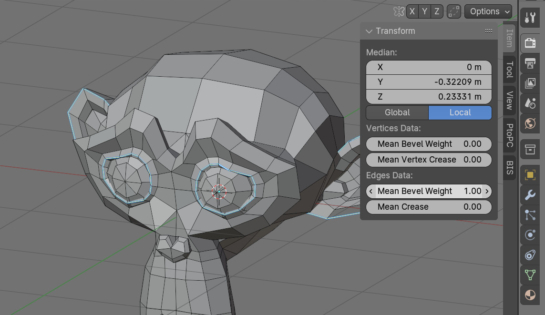
 .blend file on Patreon
.blend file on Patreon