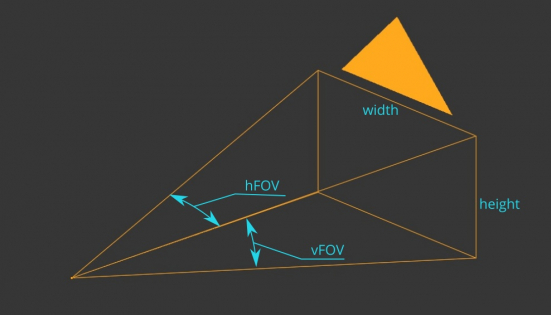
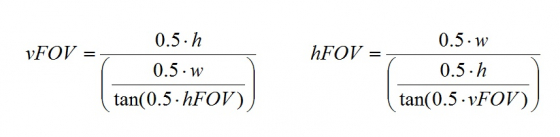Cameras in Blender are always defined by two FOV angles – vertical and horizontal.
One of these angles is always set by the user through the camera parameter – Feild of View (or a combination of the Focal Length and Sensor Width parameters).
What kind of angle it will be – vertical vFOV or horizontal hFOV – depends on the aspect ratio of the render.
|
1 2 3 |
render_width = bpy.context.scene.render.resolution_x render_height = bpy.context.scene.render.resolution_y aspect = render_width / render_height |
If the Aspect Ratio is greater than 1, the camera parameters determine the horizontal FOV (hFOV). If the Aspect Ratio is less than 1, the vertical FOV (vFOV) is set by the camera parameters.
If we know one of the camera’s FOV angle, we can always find another angle using the following formula:
Where:
w – horizontal render resolution (width) in pixels
h – vertical render resolution (height) in pixels
With these expressions we can calculate both FOV angles for the camera:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
import bpy import math camera = bpy.context.active_object render_width = bpy.context.scene.render.resolution_x render_height = bpy.context.scene.render.resolution_y aspect = render_width / render_height if aspect > 1: hFOV = camera.data.angle vFOV = 2 * math.atan((0.5 * render_height) / (0.5 * render_width / math.tan(hFOV / 2))) else: vFOV = camera.data.angle hFOV = 2 * math.atan((0.5 * render_width) / (0.5 * render_height / math.tan(vFOV / 2))) print(math.degrees(vFOV), math.degrees(hFOV)) # 53.13 90.0 |